Glucose Monitor for Dogs: How Tracking Blood Sugar Works (Vet Verified)
Diabetes in dogs is cunning, and every change in the glucose levels can impact not just how dogs feel, but their insulin dose as well. If glucose levels plummet, it could mean the dose is too strong, or, if the levels are high, it can leave them thirsty, tired, and prone to more serious complications. To keep a better track of these changes, pet owners use a glucose monitor for dogs, a tool that measures glucose levels, helps determine blood glucose curves (BGCs), and more. We’ll show you the different types of these monitors, how they work, and more.
Key takeaways:
- Glucose levels guide how diabetic dogs feel and how well their insulin plan is working.
- Pet owners can monitor glucose using either handheld glucometers or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs).
- Glucometers give quick, single readings, while CGMs reveal full-day trends and patterns.
- Monitoring daily habits such as thirst, energy, and sleep helps spot early signs of changes in blood sugar.
- Tools like Maven Pet add another layer of insight by tracking behavior shifts that often precede glucose swings.
Why Diabetic Dogs Need Glucose Monitoring

Diabetic dogs need glucose monitoring because those numbers show how well their insulin plan is actually working. Blood sugar can fluctuate by the blink of an eye, and catching those changes early helps keep them safer and feeling better day to day.
Take a dog on Caninsulin or Vetsulin, for example. You might stick to the same dose every morning, but that doesn’t always make sense. Maybe they didn’t finish breakfast, got extra exercise, or were stressed by a loud delivery truck. Any of that can turn their glucose levels topsy-turvy. Monitoring helps you see those shifts instead of guessing.
Types of Glucose Monitors for Dogs
There are two main types of blood glucose monitors for dogs: handheld glucometers, which use a tiny drop of blood on a test strip, and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), which track levels through a small sensor on the skin. Both give you valuable information, just in different ways.
Glucometers
Glucometers are handheld tools that most people picture when they think about checking blood sugar. Here’s how they work. You get a tiny drop of blood from your dog’s ear with a sterile lancet or hypodermic needle. You place the drop on a test strip and insert it into the glucometer to get a quick snapshot of your dog’s glucose level at that moment.
They’re simple, budget-friendly, and great for those routine spot checks or at-home glucose Blood Glucose Curves (BGCs) your vet may ask for. These curves represent charts for tracking the dog’s blood sugar levels, usually over the course of 12 to 24 hours, so that the vets can find the lowest point or nadir, the dangerously low points (hypoglycemia), or highs (hyperglycemia).
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
CGMs take a more modern, hands-off approach. A small sensor sits on your dog’s skin and quietly tracks glucose levels in the surrounding tissue fluid all day long. Instead of just one number here and there, continuous glucose monitoring for dogs gives you the whole story: where their levels rise, where they dip, and how steady things stay between meals and insulin doses. Devices such as the FreeStyle Libre are commonly used for this type of monitoring.
“I got the Maven sensor for my 14-year-old Chihuahua mix with heart and trachea issues. It gave me back peace of mind – I can track her RRR, BPM, drinking, and activity anytime and know instantly if something’s wrong. Highly recommend!”

★★★★★
Chiara De Luca
Titti
Blood Glucose Monitor for Dogs: How It Works
Although both types of blood glucose monitors for dogs share the same goal, they achieve it in different ways. Traditional glucometers rely on the process called amperometry, a process that’s the basis of how electrochemical blood glucose meters work. When blood contacts the strip, a small electrical current is generated, and the meter measures this signal to calculate the glucose level. It all happens in just a few seconds, so that you can get a real-time reading.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) operate slightly differently. Instead of measuring blood directly, the sensor sits on the skin and monitors glucose levels in the fluid between cells (interstitial fluid). As glucose moves in and out of this fluid, the sensor tracks those changes and sends updates every few minutes.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Dogs: Pros & Cons
Like any tool, CGMs have strengths and limitations. Here’s a quick look at what they do well and where they may fall short.
Pros
- Provide near-real-time glucose updates throughout the day
- Show helpful trend patterns, not just one-off readings
- Reduce the need for frequent finger-pricks
- Make it easier for you and your vet to fine-tune insulin dosing based on actual daily patterns
Cons
- Typically more expensive than traditional glucometers
- Sensors can occasionally fall off, especially on active or itchy dogs
Dog Glucose Monitor at Home: What Owners Should Know

When you’re checking your dog’s glucose at home, it helps to know the general goal. Healthy dogs can have their glucose levels between 80 and 120 mg/dL, while most diabetic dogs do best when their levels stay roughly 100–250 mg/dL during the day.
Your dog’s everyday habits also tell a story. Increased thirst, peeing more than usual, often signals higher glucose levels, while sudden shakiness, wobbliness, or odd behavior can point to a dip. Appetite, energy, and water intake are surprisingly good “early warning” clues that something might be shifting.
To keep track of everything, many pet parents use a diabetes diary or a pet health app to log meals, insulin, and readings. A CGM can make this even easier by automatically collecting most of that data and showing trends, highs, and lows without you having to log every detail. It’s a simple way to stay ahead of changes and keep your pup feeling their best.
How Vets Use Glucose Curves & Daily Readings
“Glucose monitors help track the numbers, but changes in behavior—like restlessness, sleep shifts, or activity drops—often signal blood sugar swings first.” — Carolina Domingues, DVM, Veterinarian at Maven Pet
Vets use glucose curves and daily readings to see how your dog responds to insulin over a whole day. These curves show where the glucose starts, how low it goes, and when it rises again. With a glucometer, this usually means taking a reading every 1–2 hours after an insulin dose and after a meal to track highs and lows. That curve helps your vet decide if the dose is correct, if the timing needs tweaking, or if something else is affecting your dog’s stability.
Now, with CGMs, veterinarians receive glucose data from the sensor throughout the day, providing a continuous view of trends. They can see exactly when your dog dips, when they spike, and how long they stay in the target range.
How Maven Pet Helps Track Early Signs of Blood Sugar Changes
Maven’s dog health tracker doesn’t measure glucose itself, but it’s excellent at spotting the little shifts that often happen when blood sugar starts going up and down. It keeps an eye on your dog’s activity, rest, heart rate, and breathing, and these things can quietly change long before you’d notice on your own.

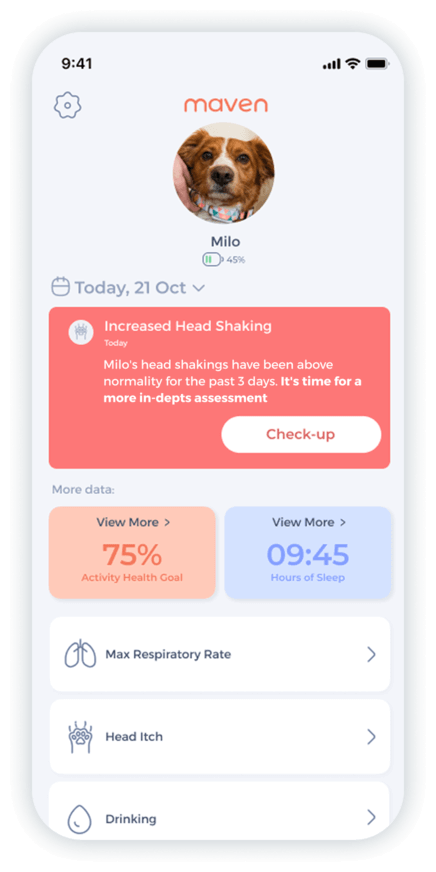
Monitor heart rate, respiratory rate, activity & rest, drinking, itch behavior.
If your dog’s energy suddenly drops, Maven picks it up through lower movement and excited-time scores. If their sleep gets choppy, the night-rest insights flag those extra wake-ups. And because Maven learns your dog’s personal baseline, alerts only pop up when something truly strays from their usual rhythm.
When Maven detects a meaningful change, it checks in with quick, guided questions, then packages everything into a simple weekly summary for your vet. That makes it easier for your veterinarian to fine-tune your dog’s diabetes plan.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes in dogs becomes much easier when you understand how glucose levels shift and how tools like glucometers, CGMs, and daily behavior tracking work together. The key is to watch trends, stay consistent with monitoring, and loop in your vet. That’s the only way you can keep your dog steadier and feeling their best. And if you want early clues when things start to change, Maven’s smart collar adds that extra layer of insight to support your dog every day.
Maven Pet focuses on improving the quality of life of our pets with technology, using artificial intelligence (AI) to enable proactive pet care. By accurately collecting and monitoring pet data 24/7 and flagging any irregularities, Maven Pet empowers pet parents and veterinarians to stay ahead of potential health issues, ensuring the well-being and longevity of our beloved companions.




